In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is the most effective, commonly performed and final infertility treatment in the world. However, unless you’ve been through this, most people don’t really know what the steps involved with this assisted reproductive technology (ART) entail. You can consider this your introductory guide.
First, IVF is a sequence of procedures that involves fertilizing an egg outside of a woman’s body in a specialized laboratory. It is often done after other methods of trying to get pregnant have failed.
This is how IVF works, step by step:
Preparing for an IVF Cycle – Testing and Ovarian Stimulation
Before IVF, an evaluation of the uterus and fallopian tubes will be done to make sure there are no problems that require surgical repair. Pre-cycle tests include a hormonal evaluation to assess thyroid function and ovarian reserve, detection of sexually transmitted infections in both partners, and semen analysis of the male partner.
Most women will take fertility drugs for ovarian stimulation for 8-14 days; The average is 10-11 days. Ovarian stimulation is used to mature multiple eggs for egg retrieval. Even if ovulation is normal, fertility drugs are used to produce more than one egg because pregnancy rates are higher with more eggs. Typically, an average of 10 to 20 eggs is retrieved for IVF. However, not all of them are viable to use, since on average only two-thirds are of adequate maturity.
Your doctor will carefully design a protocol to try to obtain the maximum number of eggs while protecting against the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Fertility drugs for IVF are usually injected, and you will be monitored frequently using hormonal tests and vaginal ultrasounds for the best result. Once an ultrasound determines that you have a sufficient number of follicles large enough and your estrogen level is at the correct level, you will receive an injection of hCG or another medication. This replaces a woman’s natural increase in luteinizing hormone that stimulates the final stage of egg maturation, so the eggs can be fertilized.
Egg retrieval
Thirty-four to thirty-six hours after receiving the trigger injection, before the eggs ovulate, you will have a surgical procedure to remove the eggs from the follicles in the ovaries. For this egg retrieval procedure, an ultrasound is used to visually guide a small needle through the top of the vagina to one ovary and then the other. You should not experience any pain or discomfort during the process as you will be under intravenous sedation while being closely monitored by an anesthesiologist.
The follicles are entered with the needle and the contents of the follicular fluid are removed using a gentle suction that brings the egg into the fluid; The entire process generally takes less than 30 minutes. You may experience mild colic on the day of the procedure, which usually goes away the next day. There may be a feeling of fullness and/or pressure due to the expansion of the ovaries by ovarian stimulation. This can last for a few weeks.
The fluid from the follicles, which contains the egg, is aspirated by the IVF doctor through small tubes and into a test tube. The test tube is then delivered to an embryologist who uses a microscope to find the egg in each test tube of follicular fluid. All details of the eggs are carefully recorded. The number of eggs produced and removed depends on the patient’s age, ovarian reserve, response to ovarian stimulation, and sometimes the ability to access the ovaries with the needle.
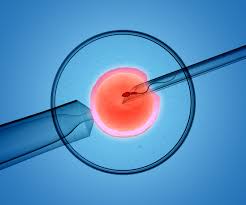
Fertilization
Once the eggs arrive in the laboratory, experts examine them to determine maturity and quality. The mature eggs are transferred to a special culture medium, placed in an incubator, and a few hours after the egg is removed they are fertilized with sperm. There are two ways to fertilize an egg: conventional insemination or intracytoplasmic injection (ICSI). The IVF team (doctors and embryologists) will determine which process will be used and will depend on multiple factors related to the partner who goes through IVF. Both methods have approximately the same success rate. ICSI is used approximately 70% of the time when factors make fertilization less likely due to poor semen quality or prior failure of IVF
For the conventional method, sperm are placed in the culture medium.
Follow Us

Add Your Comment